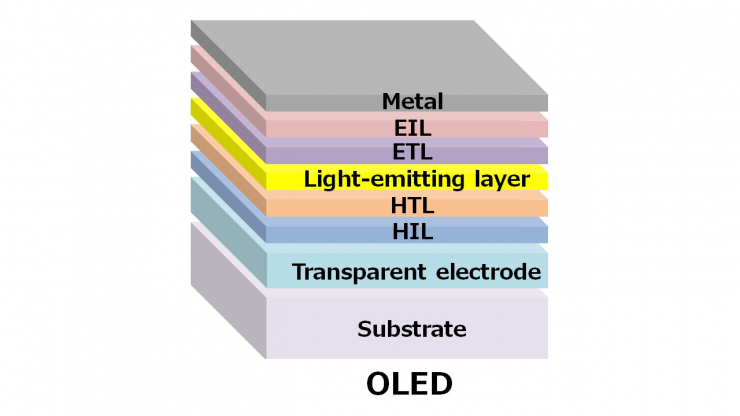
OLED is a solid-state, semi conductive device which is made up of light-emitting organic materials when the electric current passes through it. OLED is an abbreviation of Organic Light Emitting Diode.
OLED is operating like diodes and LEDs. The difference is OLEDs are used organic molecules to produce electron and electron gaps.
OLED is made up of carbon-based organic material with light-emitting properties which is located between an anode and a cathode. Although more layer is used in OLED which is developed to be more efficient, the basic principle remains the same.
When the electric current applied, electrons pass from cathodes to anodes and passes through the organic layer between them. By this way, organic layer starts to emit light.
Selection of organic material will designate the wavelength of the light in other words its color. The combination of layers which emits blue, red and green will create OLEDs that emits white light.
OLED is thinner than 500 nm. It can be said that it is 200 times thinner than human hair. It is possible to create thin lighting panels by OLED technology. These panels can be flexible and transparent structure.
The significant advantage of OLED is that it is thin and highly efficient. In this way, it is used in many areas. OLEDs are usually used in TV’s, computer and mobile phone screens, automobile headlights and automobile screens. OLEDs are preferred to be used in general lighting applications.
It is possible to do high-quality lighting which is closed to natural sunlight with OLEDs. In addition to this, OLEDs have high color rendering index performance. The objects under the OLED light are observed closer to their natural color.
OLEDs are UV resistant and release less heat. OLED has low glare value. It provides soft and natural light distribution.






COMMENTS
MAKE A COMMENT