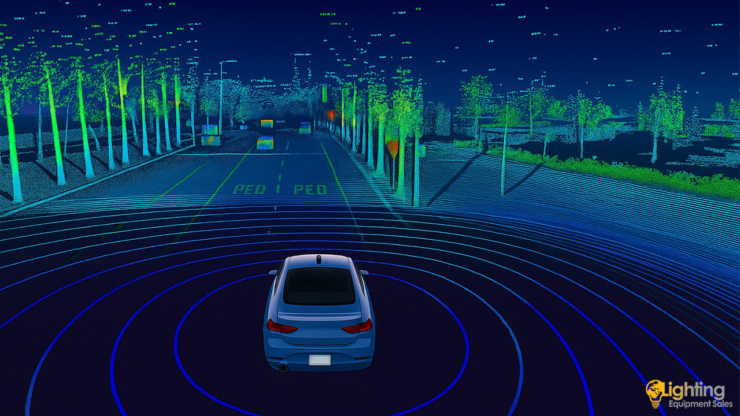

What is a LIDAR Sensor? How It Works and Where It’s Used
The LIDAR sensor is one of the core technologies frequently mentioned in autonomous vehicles, defense industry, mapping systems, and smart city solutions. LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a sensing technology that measures distance using light waves. It typically consists of a laser emitter, a receiver sensor, and a control unit. LIDAR emits laser beams toward surfaces, and by calculating the time it takes for the beams to hit an object and bounce back, it determines distances with high precision.
LIDAR technology uses laser beams that are safe for human eyes. It can detect the x, y, and z coordinates of any object it interacts with. Unlike radar systems, which use radio waves, LIDAR sensors operate with laser beams. This allows them to perform more accurate measurements and detect smaller objects.
How Does a LIDAR Sensor Work?
- Laser Emission: The LIDAR device emits numerous infrared laser beams in all directions.
- Signal Reflection: When a beam hits an object, it reflects back and is captured by the sensor.
- Time Measurement: The time between emission and reception is measured precisely.
- Distance and Position Calculation: Based on this time, the system calculates the object’s distance and position. Thousands of beams generate a detailed 3D map of the environment.
Differences Between LIDAR, Radar, and Cameras
The main differences between LIDAR, radar, and camera systems lie in their working principles and application areas. LIDAR uses laser beams to measure distances with millimeter-level precision. Radar uses radio waves, which provide longer range but lower resolution data. Cameras capture visual imagery, offering color and texture but are dependent on lighting conditions. LIDAR excels in 3D mapping and environmental modeling; radar performs better in adverse weather; and cameras are helpful for object recognition, usually in combination with other sensors for depth perception.
Where is LIDAR Used?
- 🚗 Autonomous Vehicles
LIDAR acts as the “eyes” of self-driving vehicles, offering environmental awareness by detecting other vehicles, pedestrians, and obstacles to ensure safe navigation.
- 🌍 Mapping and Terrain Modeling
LIDAR is widely used in generating 3D maps of forests, mountainous regions, and urban structures. It is especially valuable in geodesy, archaeology, and civil engineering.
- 🏙️ Smart City Applications
LIDAR solutions are becoming more common in traffic monitoring, security systems, and crowd management within smart city infrastructures.
- 🚁 Drone and UAV Systems
Thanks to its lightweight and high-precision design, LIDAR can be integrated into drones to perform aerial 3D scanning and analysis.
- 🌲 Agricultural Technologies
LIDAR plays a key role in precision agriculture, helping monitor plant height, analyze soil, and track crop development.






COMMENTS
MAKE A COMMENT